Active car safety features are designed to assist the driver in avoiding accidents, while passive car safety features are designed to protect occupants during a collision.
Active safety features include technologies like lane departure warning, adaptive cruise control, and emergency braking systems, which actively intervene to prevent accidents.
Passive safety features, on the other hand, include seatbelts, airbags, and strengthened body structures, which offer protection in the event of a crash.
It is essential to know how these features work in conjunction with each other to provide a comprehensive safety system for both the driver and passengers. By understanding the difference between active and passive safety features, car owners can make informed decisions to enhance their overall safety on the road.
Active Car Safety Features
Active car safety features are designed to prevent accidents by automatically responding to potential hazards on the road. These features are constantly working to enhance the safety of the driver and passengers.
Electronic Stability Control (ESC) is one such feature that helps maintain control of the vehicle by reducing skidding or loss of traction.
Another active safety feature is the Anti-lock Braking System (ABS), which prevents the wheels from locking up during sudden braking, enabling the driver to maintain control over the vehicle.
Forward Collision Warning System is another noteworthy active safety feature that uses sensors to detect the distance between the car and the vehicle in front. It alerts the driver if a collision is imminent, allowing them to take necessary evasive action.
Similarly, the Lane Departure Warning System uses cameras to monitor the vehicle’s position within the lane and alerts the driver if they unintentionally drift out of their designated lane.
Overall, active car safety features play a crucial role in preventing accidents by actively assisting the driver in avoiding potential dangers on the road.
| Active Car Safety Features | Definition and Purpose |
| Electronic Stability Control (ESC) | Reduces skidding and loss of traction |
| Anti-lock Braking System (ABS) | Prevents wheel lock-up during sudden braking |
| Forward Collision Warning System | Alerts the driver of imminent collisions |
| Lane Departure Warning System | Alerts the driver if unintentionally drifting out of lane |
Passive Car Safety Features
Passive car safety features differ from active ones by operating automatically during a collision to protect occupants. Passive car safety features are essential in protecting occupants during a crash. They are designed to minimize the risk of injury by working without any input from the driver. These features are specifically used in situations where a collision cannot be avoided.
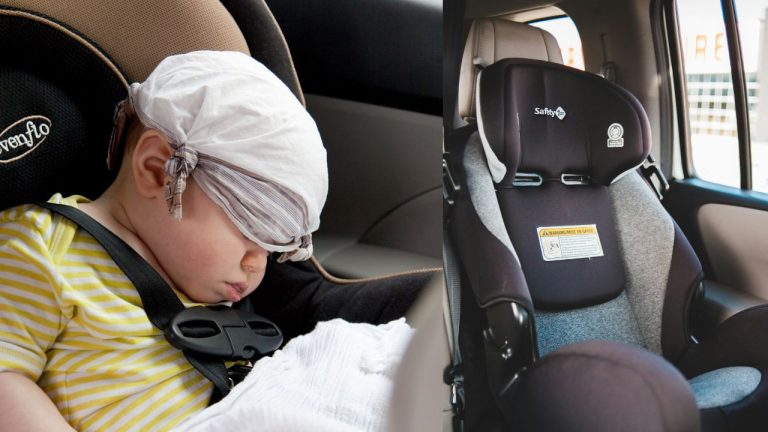
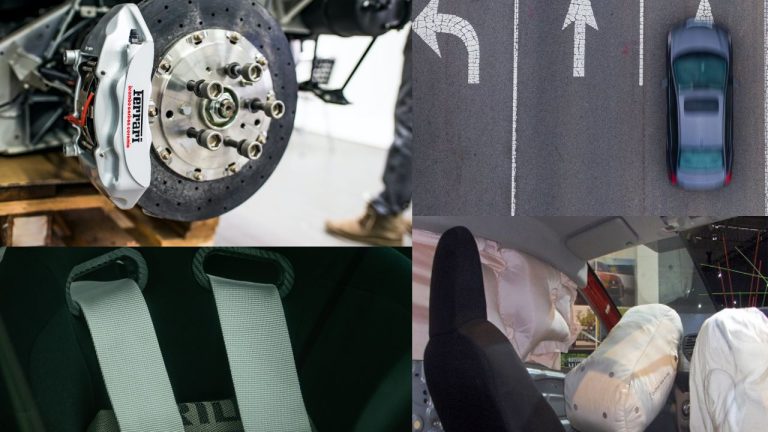
A few examples of passive car safety features include seatbelts, airbags, crumple zones, and side impact beams. Seatbelts are one of the oldest and most effective passive safety devices. They keep occupants in place during a collision, preventing them from being thrown out of the vehicle. Airbags serve as a cushion, inflating rapidly upon impact to absorb energy and protect passengers from hitting hard surfaces. Crumple zones are designed to absorb the force of impact, minimizing the transfer of energy to the occupants. Side impact beams strengthen the doors and body frame, providing additional protection in the event of a side collision.
These passive car safety features work together to enhance the overall safety of the vehicle and reduce the risk of serious injuries and fatalities during accidents. They are an essential aspect of modern automobile design that prioritizes the well-being of occupants.
Key Differences Between Active And Passive Car Safety Features
Active and passive car safety features play distinct roles in ensuring overall car safety.
- Role in Accident Prevention vs. Accident Protection: Active safety features are designed to prevent accidents by assisting the driver in maintaining control of the vehicle. These features include anti-lock braking systems (ABS), electronic stability control (ESC), and forward collision warning (FCW). On the other hand, passive safety features aim to protect occupants in the event of an accident, such as airbags, seat belts, and crumple zones.
- Activation Timing: Active safety features are typically activated and operate continually while the vehicle is in use. In contrast, passive safety features are only activated during a collision or accident.
- Driver’s Influence on Effectiveness: Active safety features rely on the driver’s actions and can be influenced by their attentiveness and response. Passive safety features, once activated, work independently of the driver’s involvement.
- Cost and Accessibility: Active safety features are often more technologically advanced and can be pricier to implement. In contrast, passive safety features are typically standard in most vehicles and readily accessible.
Both active and passive safety features are crucial for ensuring overall car safety. While active safety features focus on accident prevention, passive safety features provide protection in the event of an accident.
Conclusion
To sum it up, active and passive car safety features play crucial roles in keeping drivers and passengers safe on the road. While active features focus on preventing accidents, passive features aim to minimize injuries in the event of a collision.
By understanding the difference between the two and the importance of each, you can make informed decisions when it comes to choosing a safe vehicle. Stay knowledgeable and prioritize safety for a smoother and more secure driving experience.